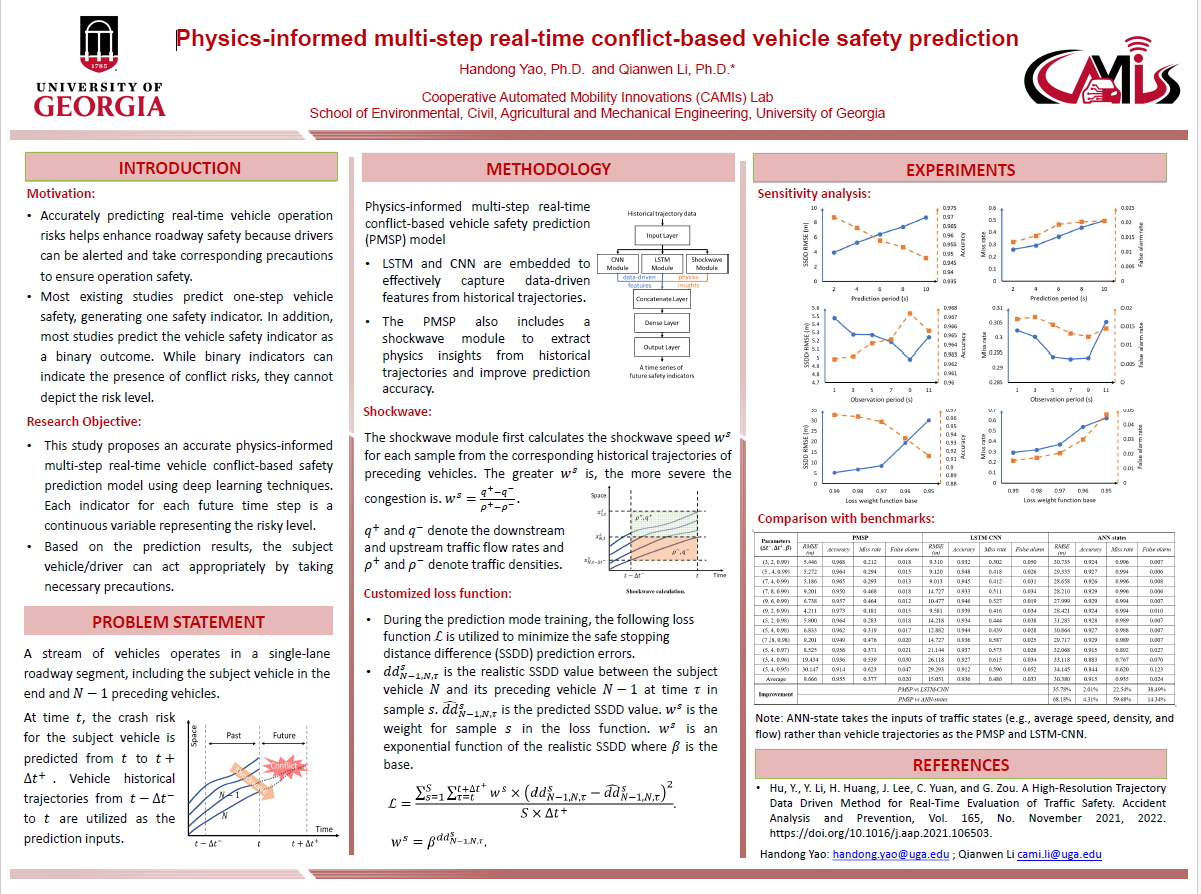
PHYSICS-INFORMED MULTI-STEP REAL-TIME CONFLICT-BASED VEHICLE SAFETY PREDICTION
PI: Qianwen Li
Co-PI(s): OT-04
Institution(s): University of Georgia
Abstract
Real-time vehicle safety prediction is critical in roadway safety management as drivers or vehicles can be altered beforehand to take corresponding evasive actions and avoid possible collisions. This study proposes a physics-informed multi-step real-time conflict-based vehicle safety prediction model to enhance roadway safety. Physics insights (i.e., traffic shockwave properties) are combined with data-driven features extracted from deep-learning techniques to improve the prediction accuracy. A time series of future vehicle safety indicators are predicted such that vehicles/drivers have enough time to take precautions. The safety indicator at each time stamp is a continuous value that the sign reflects the presence of conflict risks, and the absolute value indicates the conflict risk level to advise different magnitudes of evasive actions. A customized loss function is developed for the proposed prediction model to give more attention to risky events, which are the focus of safety management. The prediction superiority of the proposed model is proven through numerical experiments by comparing it with two benchmarks constructed based on the literature. Further, sensitivity analysis on key model parameters is carried out to advise parameter selections in developing real-world conflict-based vehicle safety prediction applications.
Please comment below with any statements or questions you may have. Also let GTI if you would be interested webinars or presentations on similar topics.