FOSTERING SMART AND SUSTAINABLE TRAVEL THROUGH ENGAGED COMMUNITIES USING INTEGRATED MULTIDIMENSIONAL INFORMATION-BASED SOLUTIONS
PI: Srinivas Peeta
Co-PI(s): OT-06
Institution(s): Georgia Institute of Technology
Abstract
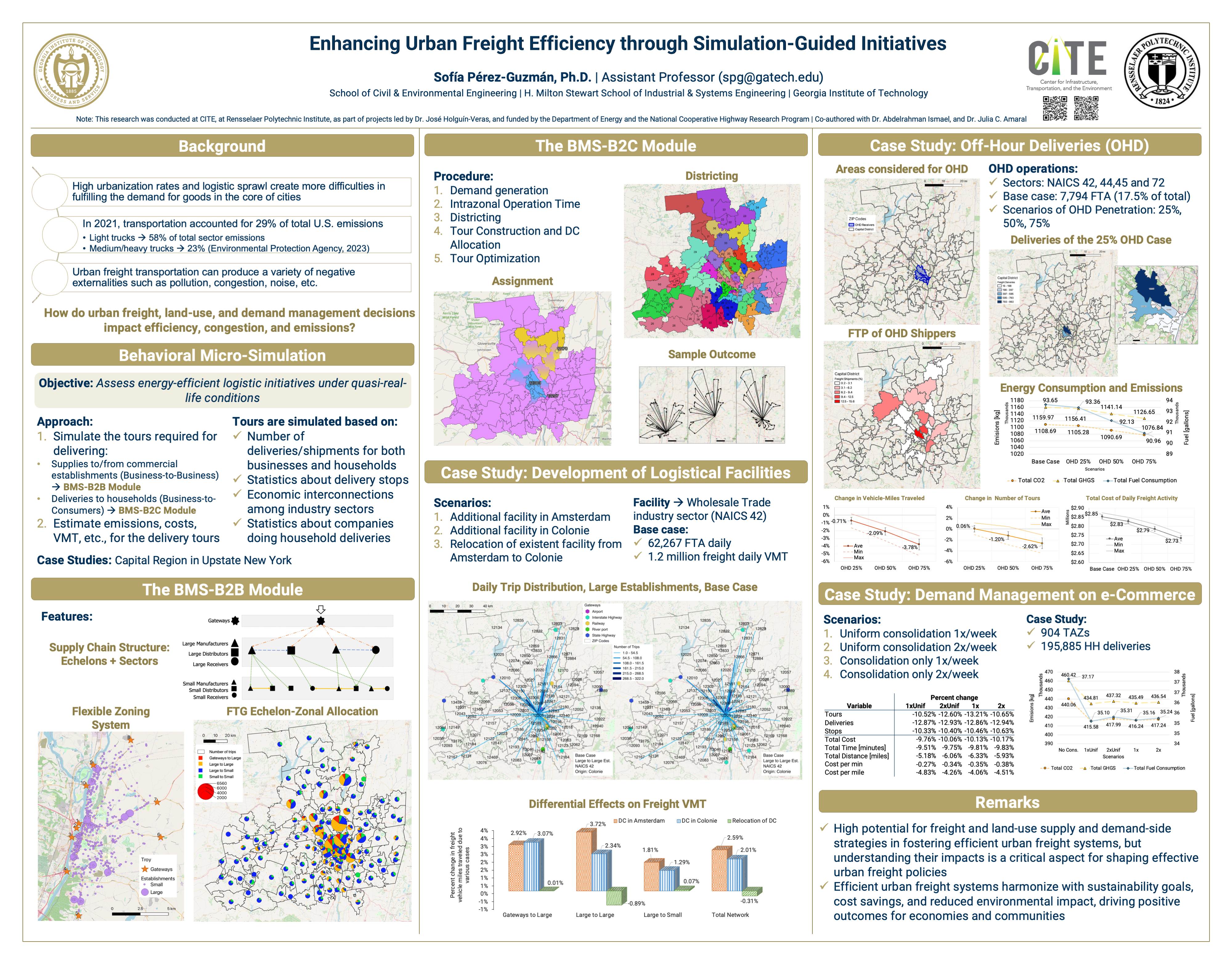
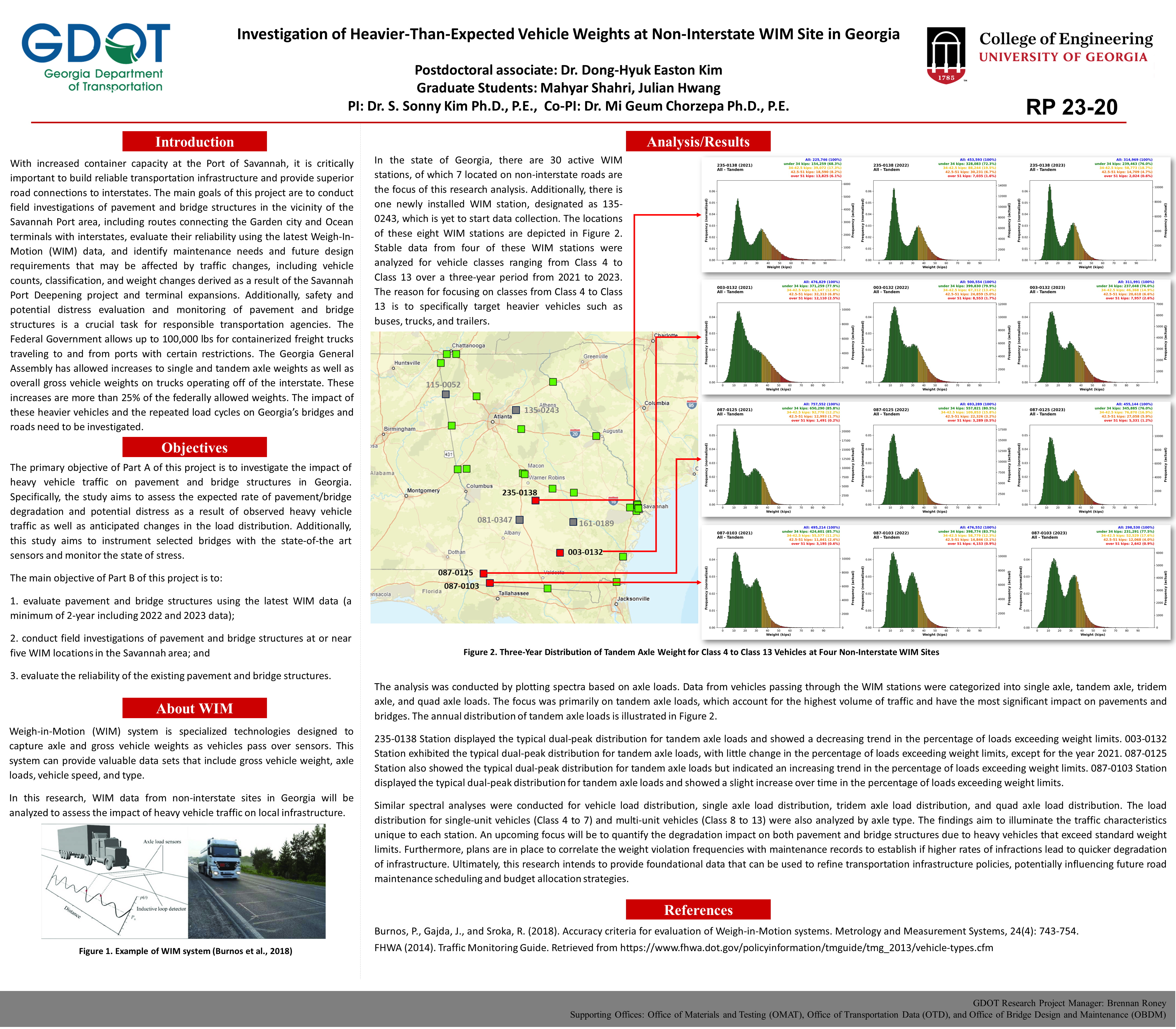
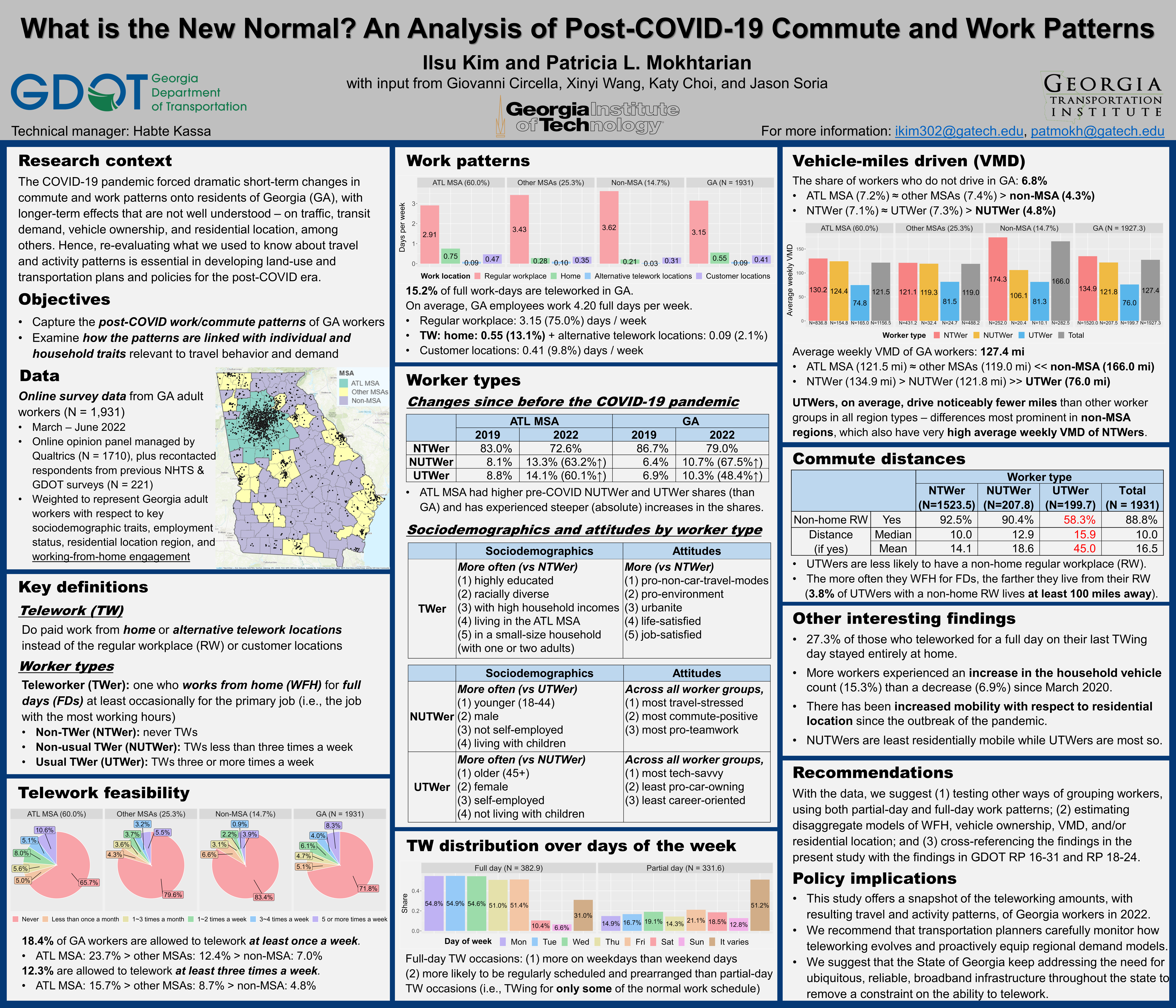
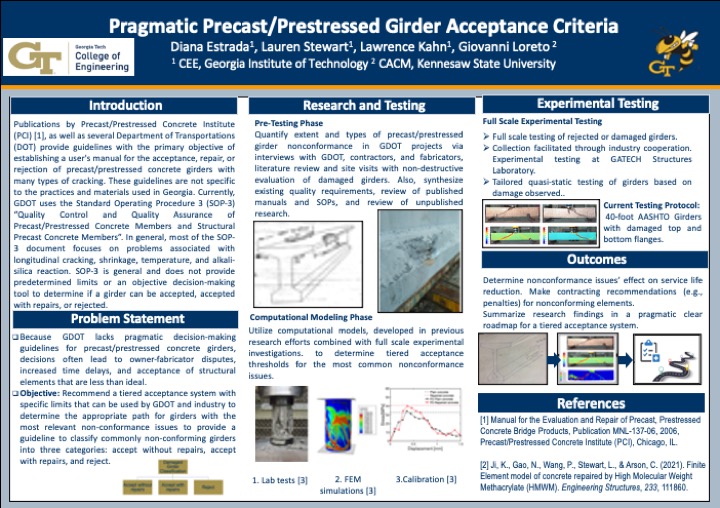
This project will develop systematic deployment tools that smart and connected communities (SCCs) can use to achieve their sustainable travel goals in a quantifiable manner by leveraging advances in information, communication, and sensor technologies. While the deployment of advanced technological solutions offers great promise for communities to improve residents’ quality of life, they encounter challenges in realizing these aspirations due to the diversity in technological and travel needs and barriers faced by the residents. Solutions to achieve sustainability objectives related to enhancing travel mobility, safety, equity, access, active lifestyle, and health will be developed using an immersive living lab (City of Peachtree Corners, GA). They include building novel partnerships involving emerging micromobility services in the private sector and the well-established public transit modes, personalized behavioral interventions to nudge and incentivize personal auto users to consider sustainable alternatives, and community level public policy interventions to enable flexible and novel travel alternatives. For underserved residents, the solutions include strategies to overcome information deserts in lower-income neighborhoods, age-related technology savviness issues for senior residents, and reduced access to smartphones and transportation options. These solutions will be developed using data collected from residents and other sources, and will be deployed using an information design system that provides targeted information to the various community stakeholders using multiple delivery mechanisms. This project seeks to foster deployment paradigms associated with holistic, community-level decision-making to achieve sustainable travel goals while meeting the needs of different stakeholders. It draws on methods from multi-objective optimization, multi-agent simulation, machine learning, behavioral economics, and data and policy analytics, to generate relevant multidimensional solutions. Further, it will lead to novel paradigms and algorithms for the solution options themselves, and for the development of generalizable principles related to practical deployment frameworks in the inherently complex SCCs.

Please comment below with any statements or questions you may have. Also let GTI if you would be interested webinars or presentations on similar topics.